Critical Care Practitioner Biology Diagrams
Critical Care Practitioner Biology Diagrams The thorax forms from the thoracic wall, its superficial structures (breast, muscles, and skin), and the thoracic cavity. A thorough comprehension of the anatomy and function of the thorax will help identify, differentiate, and treat the plethora of pathology that can occur within the thorax. The thorax is the superior part of the trunk extending between the neck and the abdomen.It consists of several components:. Thoracic wall; Several cavities; Nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics; Internal organs; Breasts; Thoracic wall. The thoracic wall consists mainly of muscles and bones that form the thoracic cage.Overall, the thoracic wall is formed by the following structures: Your thoracic cavity is a space in your chest that contains your heart, lungs and other organs and tissues. Overview Function Anatomy Conditions and Disorders Care. Contents. This layer of tissue helps protect the organs and structures inside your thoracic cavity. Conditions and Disorders.

Anatomy. Section 1. Anatomy Thorax. Plate 1-1. Plate 1-2. Plate 1-3. Plate 1-4. Before describing the anatomy of the heart, it is helpful to review other anatomic features of the thoracic cavity and organs. (T1)—gives access to the root of the neck and is not closed by a specific structure. The thoracic cage is made up of: (1) 12 thoracic vertebrae (see Chapter 3 ); (2) 12 ribs and their costal cartilages and (3) the sternum. THE RIBS. There are usually 12 pairs of ribs (i.e., the ribs that articulate with the 12 thoracic vertebrae from T1 to T12); however, there is a variation in rib number (see variant anatomy in the ribs).
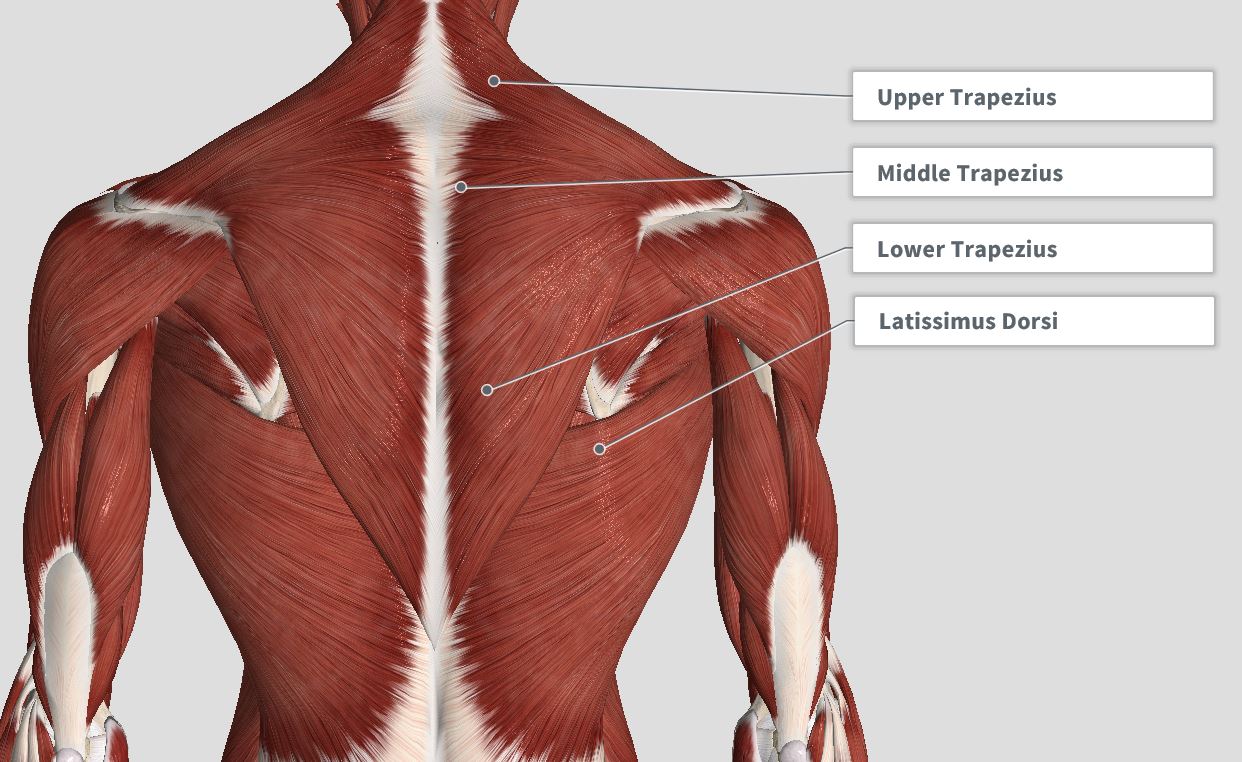
Structure, Function, Location, Anatomy, Diagram Biology Diagrams
The thorax is the area of the body situated between the neck and the abdomen. The thorax itself can be split up into various areas that contain important structures.. The thorax is bound by bony structures including the 12 pairs of ribs and thoracic vertebrae, whilst also being supported by many ligaments and muscles.. The muscles of the thorax are also important for the vital actions of Thoracic wall The first step in understanding thorax anatomy is to find out its boundaries. The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature - all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage.. The thorax has two major openings: the superior thoracic aperture found superiorly and the inferior thoracic aperture The thoracic cavity is a central compartment within the upper part of the torso, enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum.It houses vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels, as well as portions of the esophagus and trachea.. Location. The thoracic cavity is located in the chest region, extending from the base of the neck to the diaphragm, and is bounded
